本文是对文章A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition and Applications的内容摘要,主要讨论了以下四个方面:
- knowledge graph representation learning:图谱表示学习
- knowledge acquisition and completion:图谱构建
- temporal knowledge graph:时间图谱
- knowledge-aware applications:图谱的应用
1. Overview¶
知识图谱是事实的结构化表示,包含实体(真实物体或抽象概念)、关系和语义解释(semantic descriptions)。
Specific knowledge acquisition tasks¶
- knowledge graph completion (KGC)
- triple classification
- entity recognition
- relation extraction
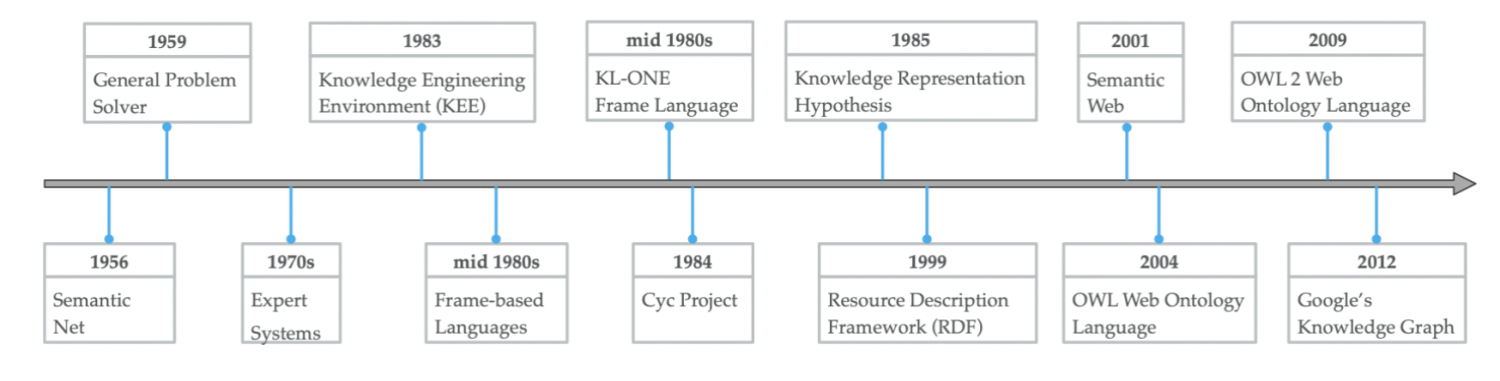
Brief history of KG¶
Defination¶
We define a knowledge graph as $x$, where $y$ and $p(y\mid x)$ are sets of entities, relations and facts, respectively, A fact is denoted as a triple $p(x,y)$.
2. Knowledge representation learning¶
Category of research on knowledge graph learning¶
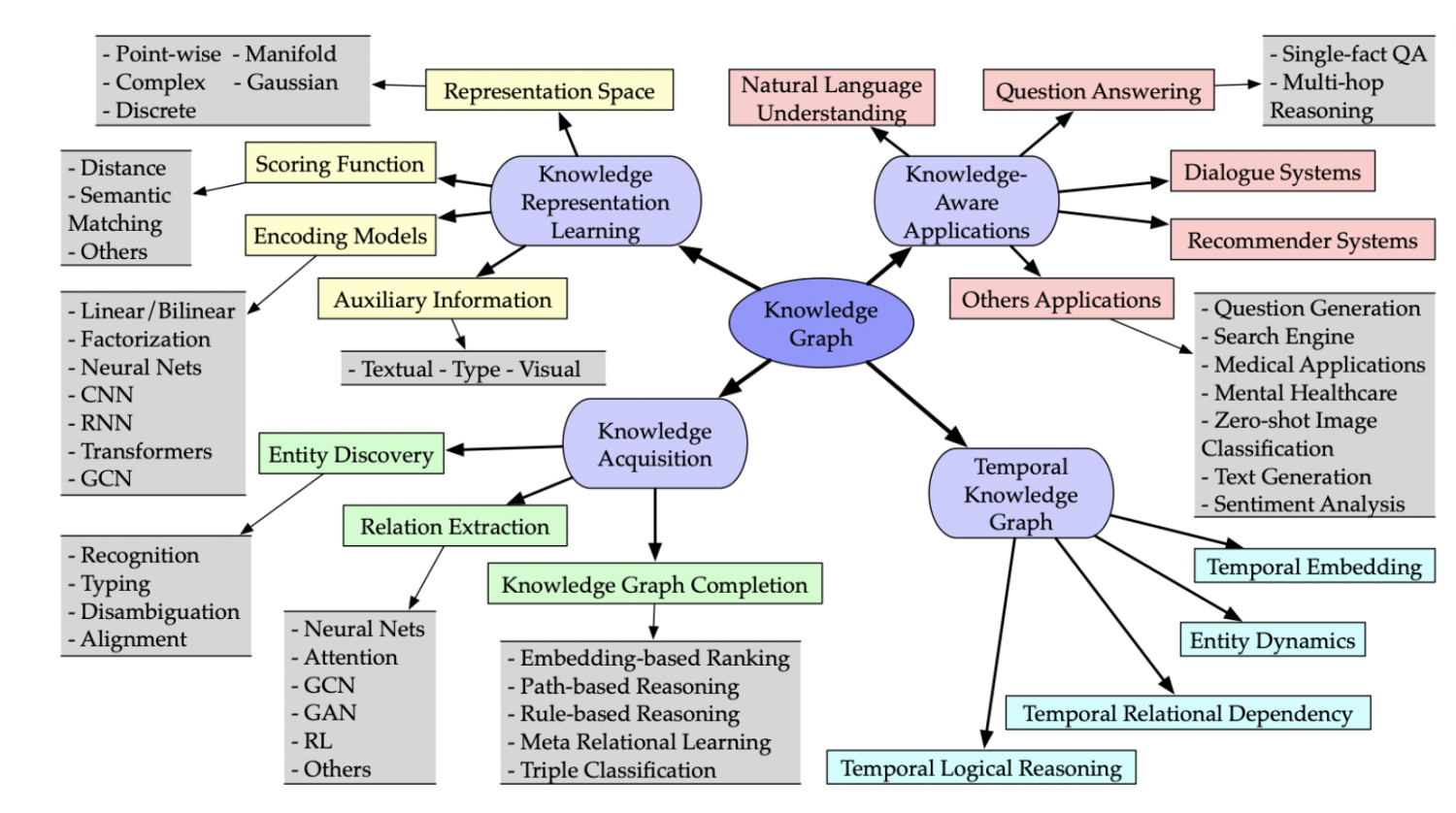
This paper mainly focus on Knowledge representation learning:
- representation space:实体、关系的表示空间
- scoring function:三元组可信度的评价指标
- encoding models:表示、学习关系之间的交互信息
- auxiliary information:其他加入编码过程的信息
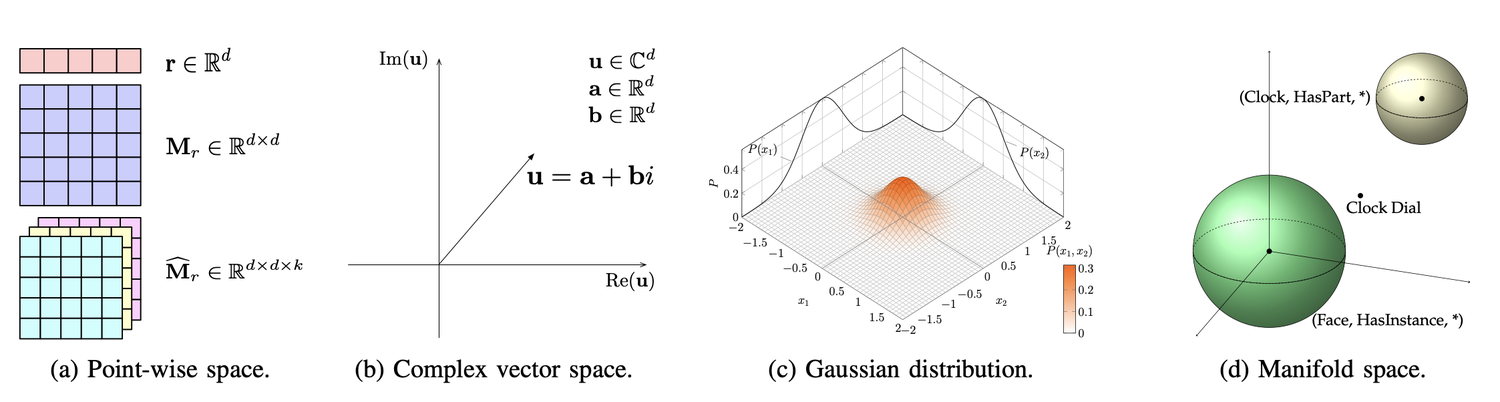
2.1 Representation space¶
Current mainly uses real-valued point-wise space, while other kinds of spaces such as complex vector space, Gaussian space, mainfold are utilized as well.
-
point-wise space (Euclidean space)
typical methods: TransR, TransR, MTN, HAKE, TransH, HolE, ANALOGY
-
complex vector space
typical methods: ComplEx, QuatE, RotatE
-
Gaussian distribution
typical methods: KG2E, TransG
-
Manifold and Group
A manifold is a topological space, which could be defined as a set of points with neighborhoods by the set theory.
Previous point-wise modeling is an ill-posed algebraic system where the number of scoring equations is far more than the number of entities and relations. Moreover, embeddings are restricted in an overstrict geometric form even in some methods with subspace projection.
typical methods: ManifoldE, MuRP, TorusE, DihEdral
2.2 Scoring function¶
Scoring function 用于评估事实(facts)的合理性(plausibility),在基于能量的学习方法中,又称为能量函数(energy function)。
Two typical scoring functions:
- distance-based (i.e., INLINEMATH4ENDINLINE)
- similarity-based (i.e., INLINEMATH5ENDINLINE)
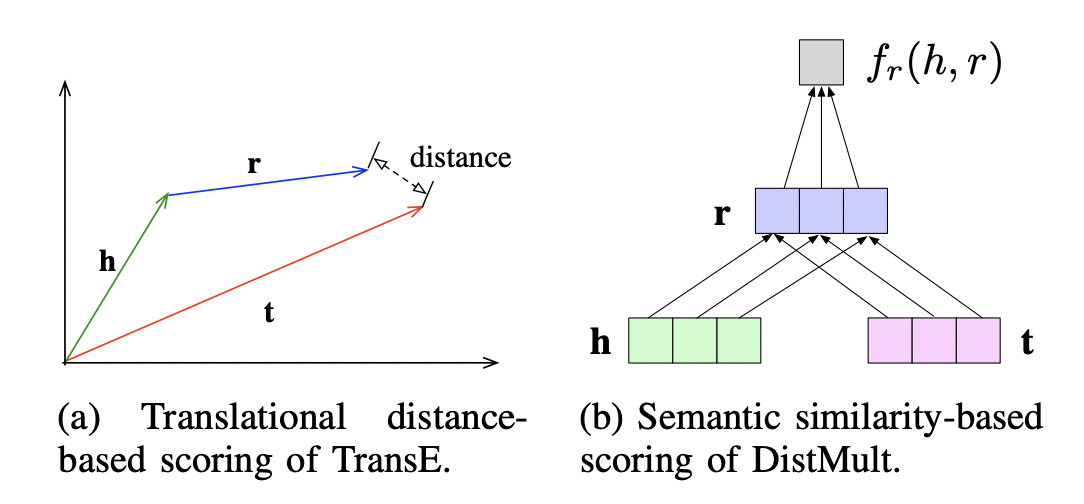
Distance-based methods: TransE, transH, TransR, TransA, TransF, ITransF, TransMS, TransAt, KG2E, ManifoldE
Semantic Matching based methods: SME, DistMult, HolE, HolEx, ANALOGY, ComplEx, CrossE, DihEdral
2.3 Encoding models¶
Aiming at encoding the interactions of entities and relations.
Typically three types of models:
-
linear/bilinear models
linear projection
-
factorization models
decompose relational data into low-rank matrices for representation learning
-
neural networks
introducing non-linearity
- CNN
- RNN
- Transformers
- GNN
2.4 Embedding with Auxiliary Information¶
-
文本信息
The challenge of KRL with textual description is to embed both structured knowledge and unstructured textual information in the same space.
Typical models: DKRL, SSP, KGE
-
类型信息
Information such as hierarchical classes or types info of entities
Typical models: SSE, TKRL, KR-EAR
-
视觉信息
Typical models: IKRL
-
概率型信息
some KG contains uncertain information with a confidence score asigned to every relation fact.
3. Knowledge acquisition¶
目标:
- 从结构化、非结构化和半结构化数据中构架知识图谱
- 图谱补全(KGC)
- 实体对齐、关系发现/挖掘
- 三元组分类、关系分类、开放图谱扩充(open knowledge enrichment)
3.1 Knowledge graph completion¶
图谱补全的子任务有:链接(link)预测,实体预测、关系预测。
- embedding-based models
-
relation path reasoning
aiming at modeling complex relation paths
-
RL-based path finding
(RL) is introduced for multi-hop reasoning by formulating path-finding between entity pairs as sequential decision making, specifically a Markov decision process (MDP)
-
Rule-based reasoning
i.e., INLINEMATH6ENDINLINE,最近的研究开始关注如何将规则融入embedding-based模型中(如KALE,RUGE,IterE,Neural-Num-LP,pLogicNet,ExpressGNN)
-
Meta Relational Learning
图谱中的关系类型分布也存在长尾现象,同时,现实世界的知识是动态变化的,这就要求我们在进行知识图谱构建/补全中考虑到这些小样本的学习,这个场景属于meta relational learning或者few-shot relation learning范畴,典型的模型有:GMatching,Meta-KGR,MetaR,GEN等
3.2 Entity discovery¶
这里的实体发现广义地指所有与实体相关的知识的获取任务。
-
(named) entity recognition(NER)
典型模型:LSTM-CNN、LSTM-CRF、Stack-LSTM、MGNER、ERNIE、K-BERT
-
entity disambiguation
也称为实体链指,典型模型有DSRM、EDKate
-
entity typing
即实体分类,包括粗粒度、细粒度两种,后者可以认为是一个多类多标签分类任务,典型的模型有:PLE、JOIE、ConnectE
-
entity alignment
aims to fuse knowledge among various knowledge graphs,典型模型有:MTransE,IPTransE,BootEA,JAPE,KDCoE,MultiKE,有关实体对齐的详细介绍,可以参考INLINEMATH7ENDINLINE
3.3 Relation extraction¶
关系抽取从非结构化文本中抽取实体间的关系事实(relational facts)并将它们加入知识图谱中,是大规模知识图谱自动构建过程中的重要任务。
由于大多数现实场景下都比较缺乏标注数据,常使用远监督(自监督、弱监督)的方式进行关系抽取,远监督使用启发式匹配的方式来进行训练数据构建,其假设为:包含相同实体引用的位置也应存在相同的实体关系。
传统的实体抽取比较依赖手工特征的构造,但近来神经网络在实体抽取中的应用越来越多。
目前比较流行的实体抽取模型概览如下:
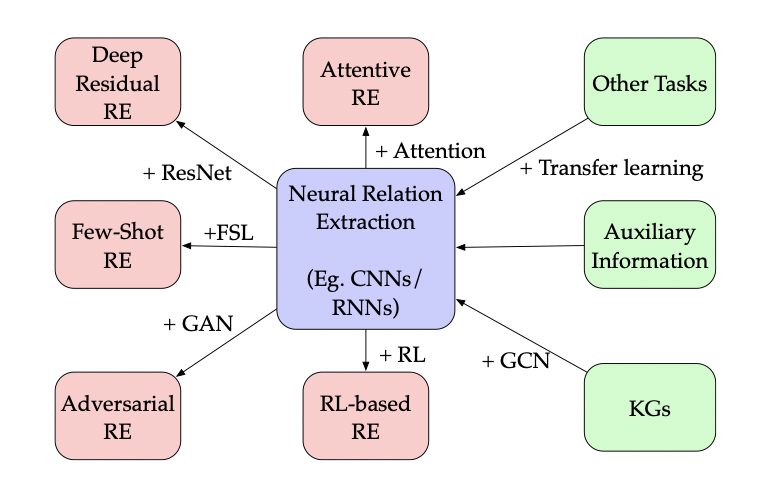
这里着重讨论一下实体抽取和关系抽取联合训练相关的模型,其中主要挑战是实体对、关系之间的重合问题,INLINEMATH8ENDINLINE提出两阶段级联标注框架来解决重合问题。另外,实体标注和关系抽取联合训练会存在训练和推理时的分布差异问题,导致标签偏置现象(exposure bias)。INLINEMATH9ENDINLINE提出了一阶段联合训练框架——将任务转化为一个token pair链接的任务,来减弱误差传播和标签偏置现象;INLINEMATH10ENDINLINE提出了一个简单有效的pipeline式的框架,独立训练两个encoder分别用于实体和关系的编码。
4. Temporal knowledge graph¶
知识图谱可以是静态的,也可以随时间发生变化。
图谱中实体、关系随时间变化的信息(temporal information)也十分重要。实体、关系随时间进化的知识图谱,这里称为temporal knowledge graph,相关的任务有:
- temporal information embedding
1 | |
-
Entity dynamics
the contextual temporal profile model [181] formu- lates the temporal scoping problem as state change detection and utilizes the context to learn state and state change vectors,相关模型如:Know-evolve,RE-NET
-
Temporal relational dependency
考虑关系链之间有时间依赖的问题:如INLINEMATH12ENDINLINE
-
Temporal logical reasoning
Logical rules are also studied for temporal reasoning,相关模型:RLvLR-Stream
5. Knowledge-aware applications¶
这里考虑知识图谱这种结构化数据的应用。可以分为两类:
- in-KG applicaitons
1 | |
-
out-KG applications:
relation extraction, QA, recommender systems
5.1 Language representation learning¶
基于自监督的大规模预训练语言模型得到了广泛的应用,但大多数都没有考虑和知识图谱进行融合的问题,ERNIE-Tsinghua、K_BERT、ERNIE-Baidu、KEPLER、GLM、CoLAKE、BERT-MK等模型在这个方向上作了一定尝试。
5.2 Question answering¶
KG-QA基于知识图谱的事实进行问题回答,可以分为以下两种:
1. single-fact QA
将知识图谱作为外部数据源,通过查询知识图谱进行简单问题的回答,如BAMnet等
- Multi-hop reasoning
多跳推理,这个方向的研究有:ConceptNet,VRN,KagNet,CogQA等
5.3 Recommender systems¶
通过融合外置信息,推荐系统可具备常识推理的能力,这有望解决推荐系统中的稀疏性问题和冷启动问题。典型模型有CKE,DKN,MKR,KPRN,PGPR,KGAT等。
6. Future of KGs¶
尽管目前对知识图谱及其相关应用研究非常广泛,以下几个问题仍然具有比较大的研究价值:
1. 复杂推理
2. 统一的框架(知识图谱的构建框架,联合实体识别,关系发现,自动构建等一系列任务)
3. 可解释性
4. 可扩展性
5. 知识聚合
6. 自动构建和维护
Refs¶
- A benchmarking study of embedding-based entity alignment for knowledge graphs
- A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition and Applications
- One model to learn them all
- A novel cascade binary tagging framework for relational triple extraction
- Tplinker: Single-stage joint extraction of entities and relations through token pair linking
- A frustratingly easy approach for joint entity and relation extraction